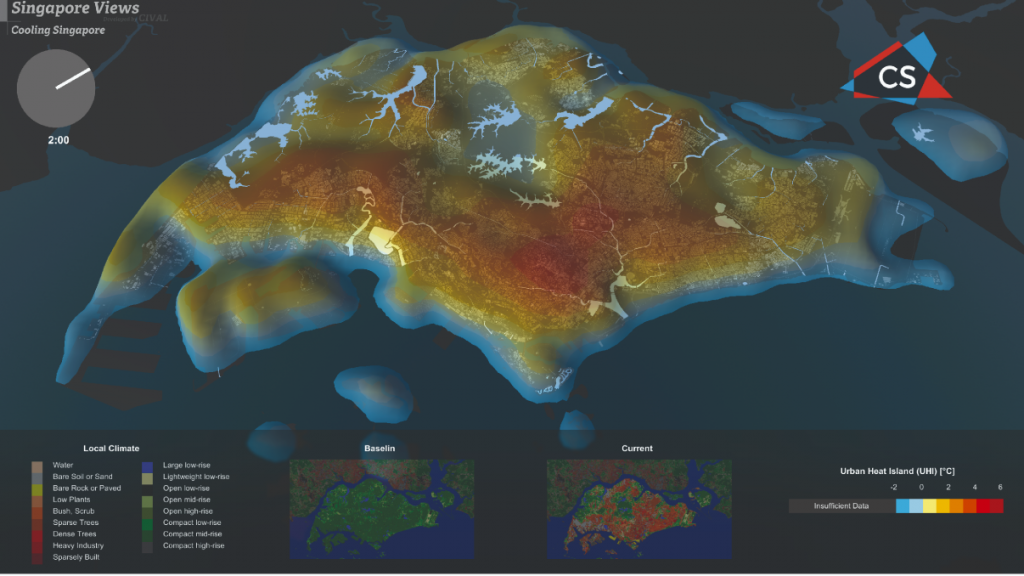
Cooling Singapore is a multi-institutional, multidisciplinary project that aims to tackle urban heat, also known as the Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect. The goal of the project is to design and implement an island-wide Digital Urban Climate Twin (DUCT) of Singapore, by developing computational models (environ- mental, land surface, industrial, traffic, building energy) as well as regional and micro-scale climate models suitable for analysing UHI and Outdoor Thermal Comfort (OTC) aspects. The project will establish climate-informed urban design guidelines as a resource to planners and agencies.
TUMCREATE researchers are developing scientific models and numerical simulations for the Energy and Transport sectors as well as machine learning models for data analytics and informed decision making. Specifically, anthropogenic heat from buildings and traffic is evaluated with the use of those models to analyse ‘what-if’ scenarios (e.g. electric vehicles, energy efficient buildings), and to explore actions which can lead to the improvement of climate in Singapore.
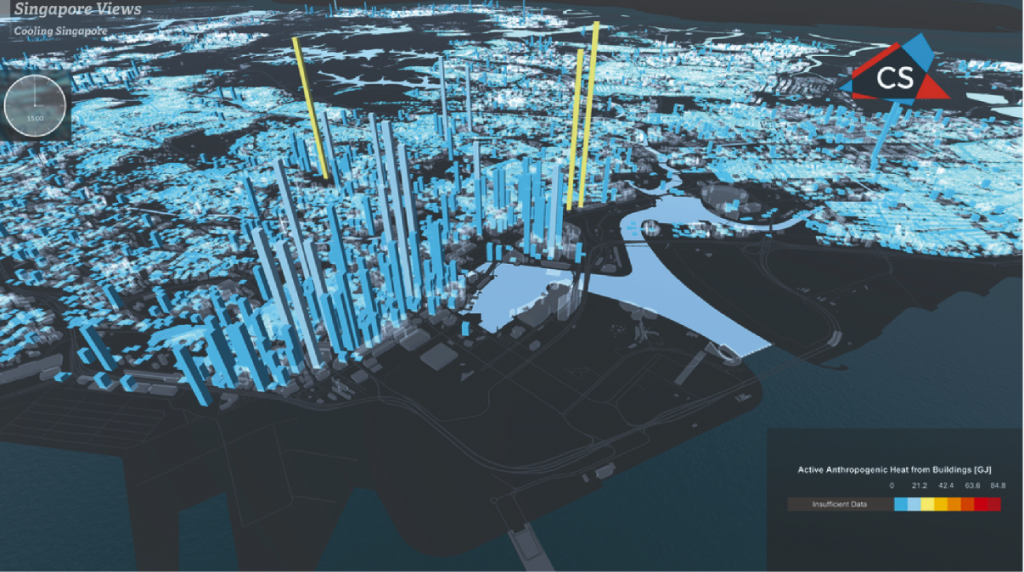
The goal of the project is to design and implement an island-wide Digital Urban Climate Twin (DUCT) of Singapore, by developing computational models (environmental, land surface, industrial, traffic, building energy) as well as regional and micro-scale climate models suitable for analysing UHI and Outdoor Thermal Comfort (OTC) aspects. The project will establish climate-informed urban design guidelines as a resource to planners and agencies. TUMCREATE researchers are developing scientific models and numerical simulations for the Energy and Transport sectors as well as machine learning models for data analytics and informed decision making. Specifically, anthropogenic heat from buildings and traffic is evaluated with the use of those models to analyse ‘what-if’ scenarios (e.g. electric vehicles, energy efficient buildings), and to explore actions which can lead to the improvement of climate in Singapore.

